To many people, hair is an important form of self-expression, and it is also an important indicator of health. Hence, hair loss can be a source of concern both for overall well-being as well as a cause for low self-esteem. There are many factors that can lead to excessive hair loss, including stress, hormonal changes, side effects of medications or treatments, as well as genetics.


Hair loss, also known as alopecia, can be divided into two categories, cicatricial alopecia and non-cicatricial alopecia [1]. Non-cicatricial alopecia is more common.
Types of non-cicatricial alopecia include:
Cicatricial alopecia refers to permanent and scarring alopecia, where hair follicles are replaced by fibrosis [1]. Cicatricial alopecia is fortunately much rarer. Available treatments for scarring alopecia are targeted at slowing down the progression of hair loss while preserving the remaining hair.
Hair loss can be temporary or permanent depending on the causes or triggers. Among the common causes of hair loss are:

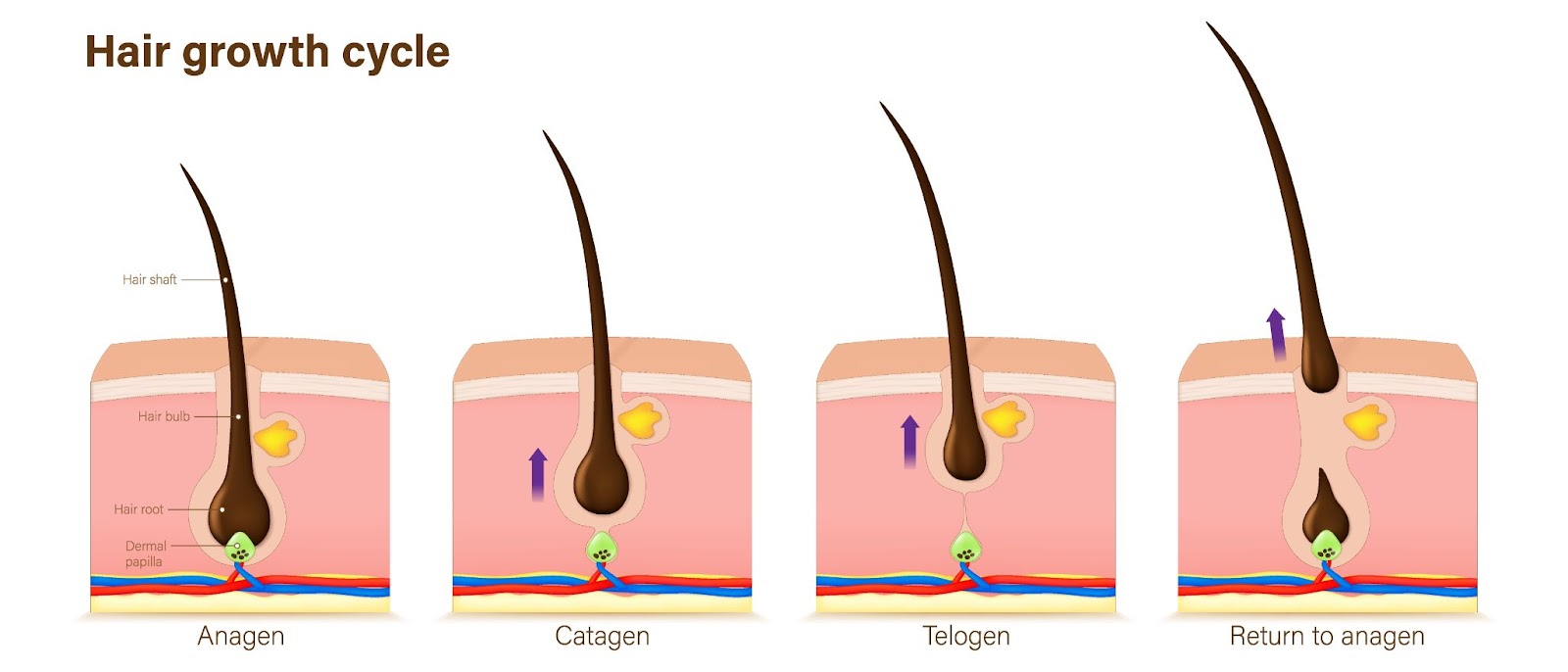
It is normal to lose between 50 to 100 strands of hair per day due to the hair growth cycle. Seeing a few strands of hair in the shower drain or your hair brush are not a cause for concern. However, if you are seeing abnormal amounts of shedding or hair loss, it may be time to visit a dermatologist.
Additionally, patches of bald spots or thinning hair can also indicate a hair loss problem.
Can my hair regrow?
Hair can regrow after hair loss if the root cause of hair loss is removed or resolved. Hereditary hair loss has no cure and may not be reversible, but treatments are available to improve hair growth and slow down hair loss.
What is the most common cause for hair loss?
The most common causes for hair loss include genetic predisposition and ageing.
Can home remedies cure hair loss?
Home remedies may help mitigate hair loss and promote hair growth, but results may vary from person to person and provide modest results.
When it comes to more significant hair loss, evidence based medical treatments tend to be more effective and can reliably yield more results. This can be beneficial in cases where hair loss is advanced or rapidly progressing.
Is surgery required for most patients with hair loss?
A dermatologist may occasionally perform biopsies to confirm the diagnosis in the minority of cases. However, most cases of hair loss can be diagnosed clinically without the need for any surgery.
Whether you’re dealing with a specific skin concern or seeking to enhance your natural beauty, Livingstone Dermatology is here to guide you on your journey to healthy, radiant skin.
Schedule an appointment today and experience the Livingstone standard of care in a welcoming, professional environment.