
Urticaria, or more commonly known as hives, is a skin condition where raised and itchy welts appear suddenly on the skin. These welts can vary in size and shape, merging into larger patches or shifting from one area to another.
While most hives fade within hours, recurrent or persistent urticaria can be frustrating and impact daily comfort. Although the condition is usually not dangerous, it can sometimes signal underlying allergies or immune reactions that need attention.
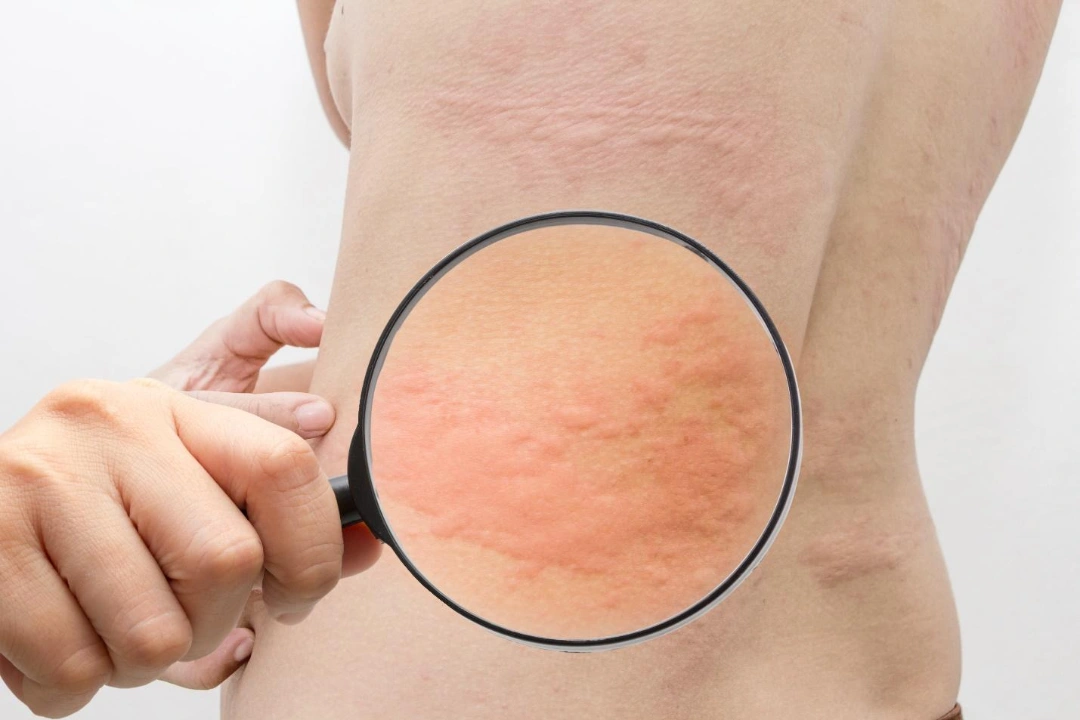
The skin condition can be classified based on its duration and triggers. These include:
Urticaria develops when certain immune cells in the skin, called mast cells, release histamine and other inflammatory chemicals into the surrounding tissue. This release causes the small blood vessels in the skin to widen and leak fluid, leading to raised, itchy welts known as hives.
In some people, this reaction is triggered by allergens such as food or medication, which the immune system mistakenly identifies as harmful. In others, the mast cells become overly sensitive and release histamine without any clear threat. This is often the case in chronic urticaria.
The underlying mechanism always involves this overactivation of mast cells, which explains the sudden onset of redness, swelling and itchiness.
While the biological mechanism behind urticaria is the same, what sparks mast cells to release histamine can vary widely from person to person. The triggers can generally be grouped into:
Food and medication-related triggers
Infection-related triggers
Physical and environmental triggers
Lifestyle and internal factors
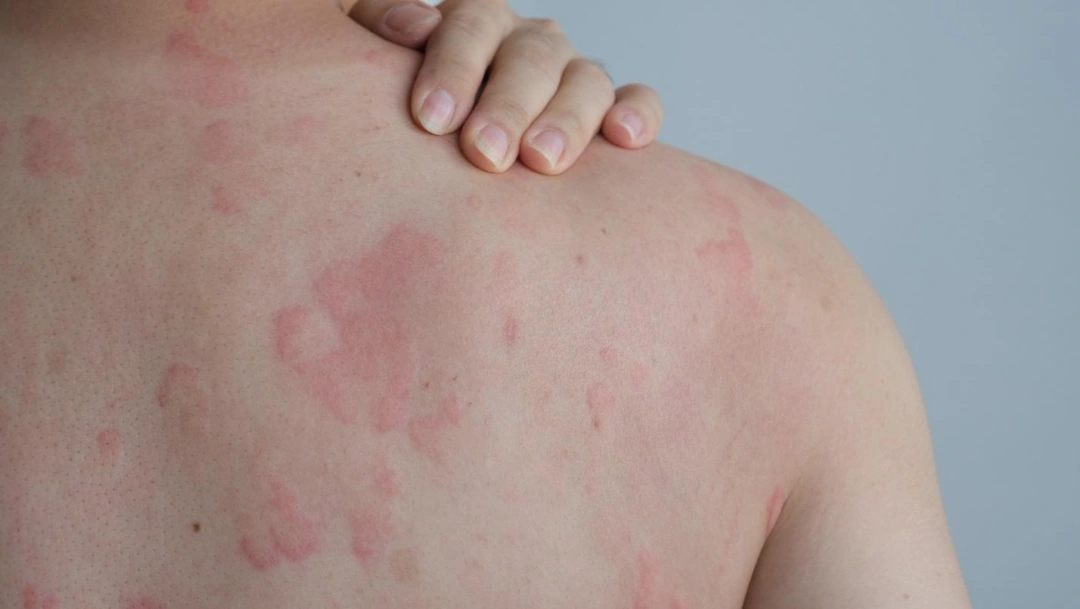
Although hives may look alarming, their features follow a recognisable pattern that helps with diagnosis. Urticaria is marked by:
This fleeting and migratory nature of hives is one of the key features that separates urticaria from other rashes.
Urticaria can affect anyone, but certain groups are more likely to experience it because of how specific factors interact with the skin and immune system. This includes:
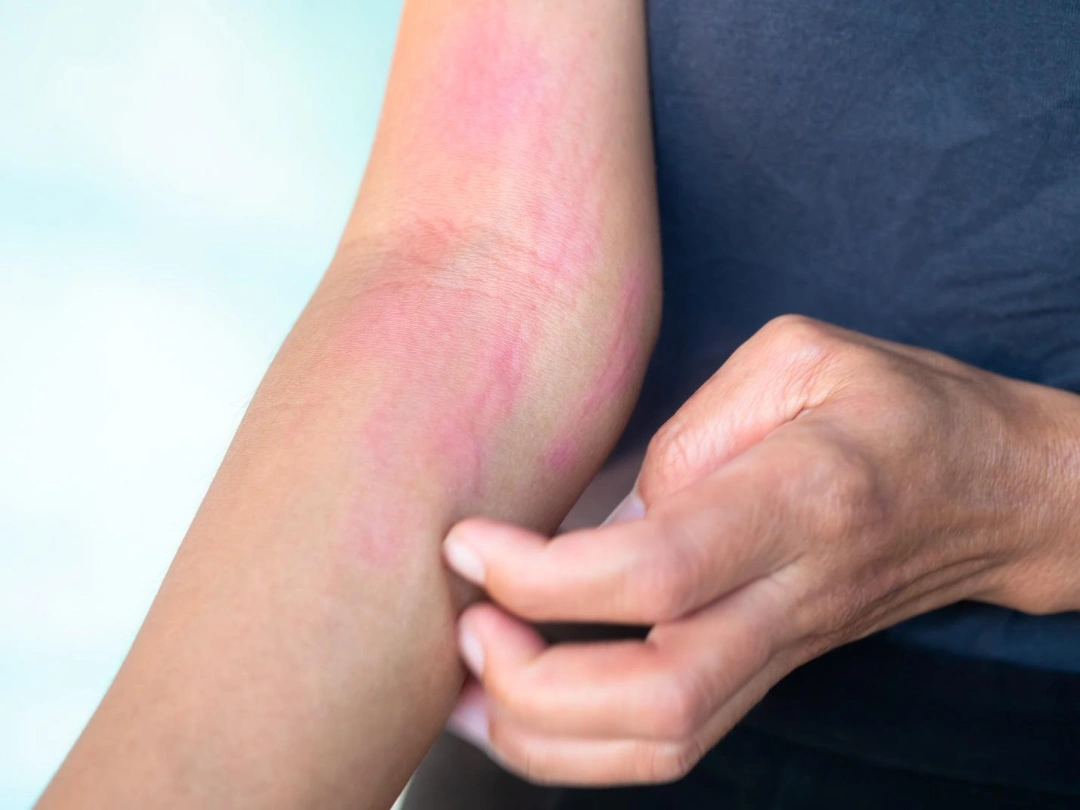
Hives can be tricky to pin down because they often come and go within hours. At Livingstone Dermatology, our approach to diagnosis is with careful questioning and tailored assessments to uncover the possible root causes. This entails:
Managing urticaria focuses on reducing symptoms, preventing flare-ups and addressing underlying triggers. Our dermatologists usually group treatment measures into supportive care, medication and modern therapies.
Some of the treatment measures include:
Lifestyle Adjustments
Medications
Specialist Treatments
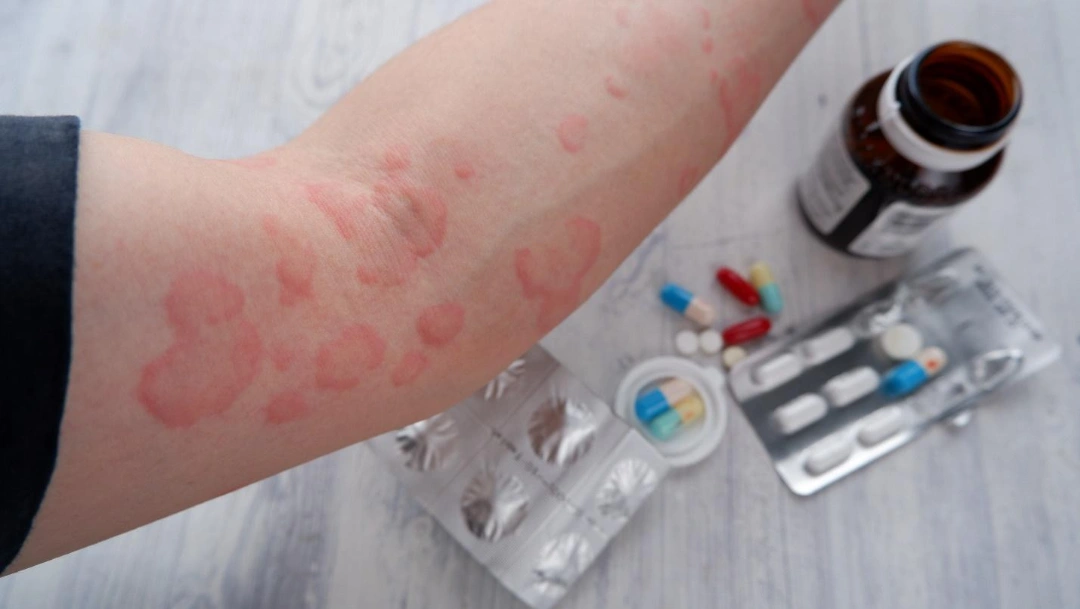
Although urticaria can feel unsettling because of its sudden flare-ups, it is a condition that can be managed effectively with the right care. Many patients find relief once their triggers are identified and a personalised treatment plan is in place. With modern therapies available, even persistent hives can be controlled to restore comfort and confidence.
If you are experiencing recurrent hives or unexplained skin swelling, know that help is available. At Livingstone Dermatology, we work with you to understand your condition, ease your symptoms and guide you towards long-term relief. Book a consultation with us today to receive effective care with a treatment plan tailored to your unique condition.
Is urticaria the same as hives?
Yes. Urticaria is the medical term for hives, which are raised, itchy welts that appear on the skin.
Can stress really cause hives?
Stress does not directly cause urticaria, but it can make mast cells more reactive, worsening existing hives or triggering flare-ups in sensitive individuals.
How long does urticaria last?
Acute urticaria usually clears within days to weeks, while chronic urticaria lasts longer than 6 weeks and may continue for months or even years. With proper management, symptoms can be controlled effectively.
Is urticaria contagious?
No. Urticaria is not an infection, so it cannot spread from one person to another.
Can food allergies cause urticaria?
Yes. Foods such as shellfish, nuts, eggs and milk are common triggers, especially in children. However, not all urticaria is caused by food, so testing may be needed before making dietary changes.
Can children develop urticaria?
Yes. Urticaria is common in children, often linked to viral infections or food triggers. The good news is that most cases are short-lived and resolve with treatment.
What is the best treatment for chronic urticaria?
For long-lasting urticaria, daily non-sedating antihistamines are usually the first step. If symptoms remain uncontrolled, advanced options such as biologic injections or other specialist treatments may be recommended.
When should I see a doctor for urticaria?
You should seek medical advice if your hives are recurrent, interfere with sleep or daily life or last longer than a few weeks. Urgent care is needed if hives occur with swelling of the lips, tongue or throat, or if you experience difficulty breathing.
Can urticaria be cured completely?
Acute urticaria often resolves once the trigger is removed. Chronic urticaria may not always have a clear cause, but with treatment, symptoms can usually be well controlled, and many patients see the condition improve over time.
Are there lifestyle changes that can help reduce hives?
Yes. Wearing loose clothing, avoiding known triggers, keeping cool in Singapore’s humid weather and practising stress management can all help reduce flare-ups.
Whether you’re dealing with a specific skin concern or seeking to enhance your natural beauty, Livingstone Dermatology is here to guide you on your journey to healthy, radiant skin.
Schedule an appointment today and experience the Livingstone standard of care in a welcoming, professional environment.