At Livingstone Dermatology, we understand that your skin is a reflection of your health and well-being. We are committed to the latest advancements in dermatological science, and dedicated to providing you with quality care.

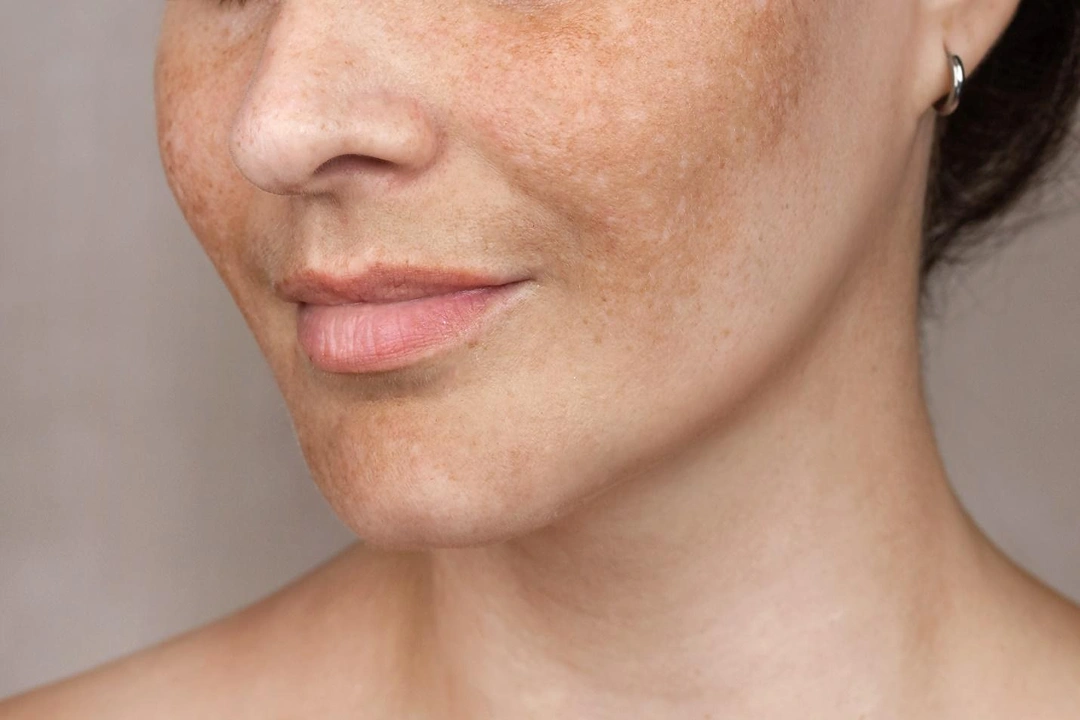
Blotchy, discoloured, or uneven skin tone is a common concern that can affect individuals of all skin types and ages. Known medically as hyperpigmentation, this condition occurs when certain areas of the skin produce excess melanin, the pigment responsible for skin colour, leading to darkened patches or spots.
Whether it is freckles, sun spots, melasma, or post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation (PIH), pigmentation issues can be triggered by a variety of internal and external factors. Though often harmless, these changes in skin tone can be distressing and may affect one’s self-confidence, particularly when they appear on the face, neck, or hands.
The good news? With the right diagnosis and targeted treatment plan, pigmentation concerns can be significantly improved and sometimes even reversed.
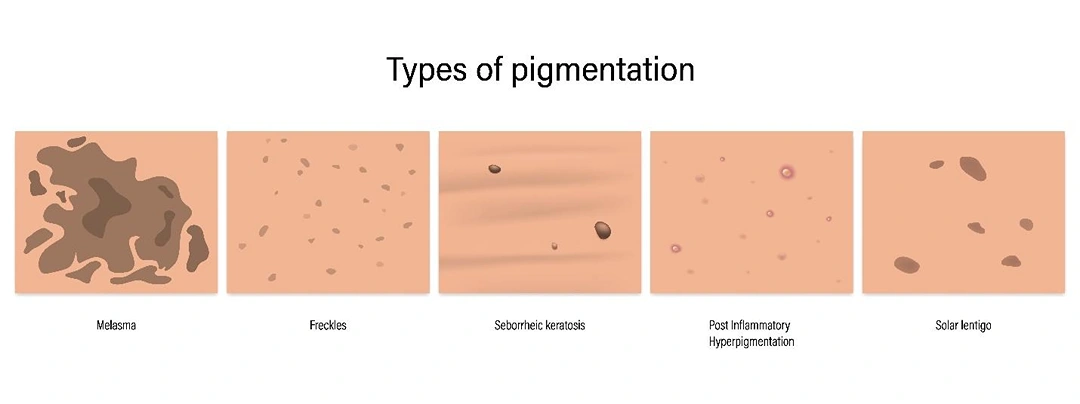
As not all pigmentation is the same, accurate identification is essential for effective treatment. Some common forms include:
Changes in pigmentation can develop gradually or appear suddenly, depending on the underlying cause. But some of the most common triggers are:
Pigmentation does not always look the same from one person to another. It can range from faint patches that fade with time to stubborn, long-standing marks that worsen with sun exposure or inflammation.
Some of the common characteristics include:
Pigmentation issues can affect anyone, but some individuals are more prone than others due to genetics, lifestyle habits, and environmental exposures. The groups more at risk include:
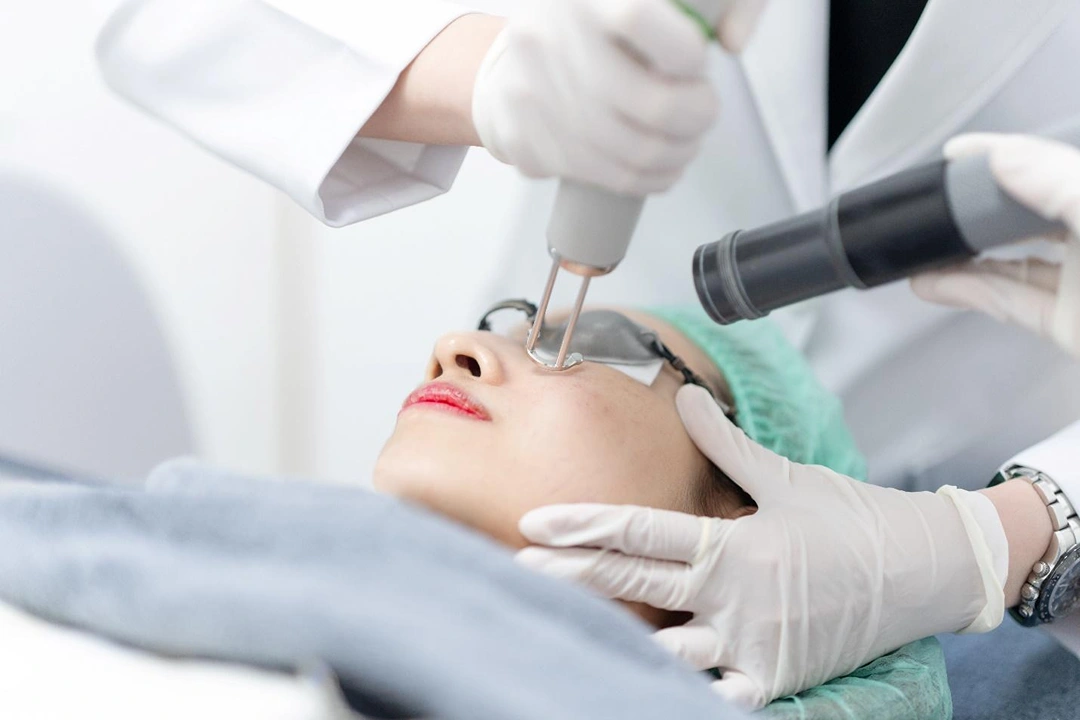
Skin disorders can be complex, and misdiagnosis may delay effective treatment. That’s why our dermatologists are committed to conducting a thorough skin assessment, which may include:
Treating pigmentation effectively requires more than a one-size-fits-all approach. The ideal treatment plan is shaped by several key factors, such as the type of pigmentation, its depth within the skin, how widespread it is, and any underlying triggers such as hormonal changes, sun exposure, or inflammation.
A personalised approach is essential. Not only does it target the pigmentation effectively, but it also minimises the risk of rebound pigmentation, skin irritation, or unintended lightening of surrounding skin. This is especially important in individuals with darker skin tones, where incorrect treatment may worsen discolouration.
Topical Treatments
Chemical Peels
Chemical exfoliants, such as glycolic acid, lactic acid, or salicylic acid, help remove the upper pigmented layers of skin and stimulate cell renewal. These are often used in a series for cumulative effects.
Laser and Light-Based Treatments
Oral and Systemic Therapies
In some cases, oral antioxidants or tranexamic acid may be prescribed to reduce melasma and prevent recurrence.
Maintenance and Prevention
Daily use of broad-spectrum sunscreen (SPF 50+), sun-protective clothing, and antioxidant skincare is vital to prevent recurrence and protect treatment results.
What results can I expect?
Improvements in pigmentation are typically gradual and depend on the type and depth of pigment, as well as the consistency of treatment. Epidermal pigmentation (closer to the skin’s surface) often responds more quickly, while dermal pigmentation may require longer and more intensive therapy.
With a comprehensive and consistent plan, most patients notice:
If pigmentation is affecting your confidence or quality of life, you do not have to live with it. With tailored, evidence-based solutions, it is possible to reduce discolouration and reclaim clearer, more radiant skin.
Schedule a consultation today and let our dermatologists at Livingstone Dermatology design a personalised treatment plan to help you achieve visible, lasting results.

Is pigmentation permanent?
Not always. Superficial pigmentation often fades with the right treatment, while deeper or long-standing pigment may take longer to improve. In some cases, ongoing maintenance is needed to keep it under control.
Can pigmentation come back after treatment?
Yes. Even after successful treatment, pigmentation can return due to sun exposure, hormonal changes, or inflammation. That is why ongoing sun protection and maintenance treatments are essential to minimise recurrence.
How can I prevent pigmentation from worsening?
Daily use of broad-spectrum SPF 50+ sunscreen, avoiding direct sun exposure, and treating skin inflammation early can help prevent pigmentation from deepening or returning. A consistent skincare routine and avoiding picking at your skin are equally important.
How long does it take to see results?
Many patients notice visible improvements within 4 to 8 weeks of consistent treatment. More stubborn pigmentation, such as melasma or dermal PIH, may take several months to lighten significantly.
Which laser is best for pigmentation?
It depends on the type and depth of pigmentation. Pico and Q-switched lasers are ideal for superficial dark spots and freckles, while fractional lasers may be better suited for deeper or more complex pigmentation issues.
Is pigmentation treatment safe for darker skin tones?
Yes, but it must be done with caution. Darker skin tones are more prone to post-treatment hyperpigmentation, so treatment should always be administered by dermatologists experienced in treating ethnic skin. Proper technique and tailored settings help minimise risks.
Can over-the-counter products treat pigmentation?
Some OTC products, such as those containing vitamin C or niacinamide, may help improve mild cases. However, more stubborn or widespread pigmentation typically requires professional evaluation and prescription-strength treatment for best results.
Whether you’re dealing with a specific skin concern or seeking to enhance your natural beauty, Livingstone Dermatology is here to guide you on your journey to healthy, radiant skin.
Schedule an appointment today and experience the Livingstone standard of care in a welcoming, professional environment.